The Cardiology Department of the CENTREDMVET Veterinary Center offers comprehensive evaluation and treatment of cardiovascular diseases in small animals by Dr Amélie Beaumier. If you are interested in scheduling an appointment please call 514-633-8888. Service hours are generally Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Saturday.
What is Veterinary Cardiology ?
Veterinary Cardiology is the branch of veterinary medicine focusing on the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular (heart and vessels) disease in animals.
This includes diseases of the heart muscle (cardiomyopathies), valvular diseases (degenerative mitral valve disease), diseases of the pericardium (pericardial effusion and tumors), congenital heart diseases, arrhythmias, systemic arterial hypertension and hyperthyroidism.
These conditions require specialized diagnostics and care in order to optimize the outcome for your pet.
Cardiac diseases are often chronic and progressive characterized by a long asymptomatic period and sudden onset of symptoms (congestive heart failure).
Furthermore, other non-cardiac diseases may be associated and may be responsible for symptoms mimicking those of hear disease.
Finally, some heart diseases may be the result of a disease originating elsewhere (infection, metabolic or hematologic disturbance, tumor).
Dre Amélie Beaumier has also extensive experience in dealing with collapsing trachea and tracheal stents.
What are possible symptoms of heart disease ?
- Coughing
- Exercise intolerance
- Rapid breathing at rest (not to be confused with normal panting)
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Difficulty resting comfortably
- Paradoxical breathing (the chest and abdmen are not moving in the same direction with breathing)
- Episodes of weakness or collapse
- Fainting spells
- Sudden inability to walk in one or more limbs with pain. This may be a sign of heart disease in cats.
- Abdominal distension
What should you do before you come to see the cardiologist ?
For your first visit please ensure that we receive all of your pet’s pertinent medical records and diagnostic tests. This includes recent radiographs (chest x-rays).
Although some tests may need to be repeated this will allow us to avoid unnecessary repetition of tests.
Please bring your pet’s current medications and do not stop any medications your veterinarian recommended prior to the visit unless otherwise instructed by your veterinarian.
What should I expect during my consultation with the cardiologist ?
In general you will first meet the cardiology technician who will collect a detailed medical history, your pet’s temperature, heart and respiratory rates and potentially a blood pressure. The cardiologist will then perform a physical examination. Based on these findings the cardiologist will provide recommendations for diagnostic tests and potentially emergency treatment.
You will be provided with an estimate for testing and treatment. An echocardiogram is performed in most cases. The goal of the cardiology consultation is to determine if heart disease is present, to stage its severity, and to ascertain that the heart disease is responsible of the symptoms that led to the consultation.
In the case where a progressive heart disease is diagnosed, a follow up strategy as well as therapeutic options will be discussed. This follow up of a disease thta may progress over several years will imply a team approach including your veterinarian and the specialist at selected times. If a noncardiac disease is suspected, the appropriate diagnostics will be recommended in order to provide a final diagnosis and an appropriate therapeutic plan. This could imply input from other specialists at the CENTREDMVET Centres (radiology, internal medicine, neurology, surgery, oncology…).
After diagnostic tests are performed the cardiologist will thoroughly discuss all the findings, diagnoses, treatment options and anticipated prognosis with you, as well as the follow up strategy. Your veterinarian will be informed of the findings and planned treatments and will receive a thorough report. Please expect the first consultation to generally last 1.5-2 hours. If extensive testing or consultations with other specialists are needed it could be longer. We try our best to stay on schedule. However, priority will be given to emergencies and rarely delays can occur.
What can be done if my pet has heart disease ?
A lot of the options for diagnosis and treatment of heart disease in people are also used in pets to prolong life and improve the quality of life. Sophisticated diagnostic tests that can be performed during an appointment such as electrocardiography, radiography and echocardiography are used to evaluate for the presence and severity of heart disease. Some heart conditions are simply monitored over time to assess for progression.
Medications may be recommended to help your pet feel better or prevent progression of disease; many of these medications are similar to those used in people.
Depending on your pet’s particular problem further diagnostics or treatments with cardiac catheterization, cardiac surgery or pacemaker implantation may be needed.
Services offered in Cardiology
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG)
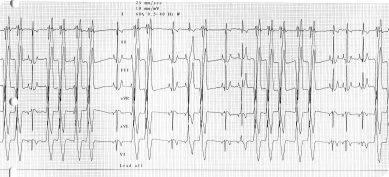
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is performed to evaluate your pet’s heart rate and rhythm in order to identify and diagnose potential rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias). For this test your pet simply needs to lie down on one side and small clips are placed on the skin.
This is non-invasive and generally does not require any sedation.
Holter (24 ECG) Monitoring
A Holter monitor is a portable continuous electrocardiogram that your pet would wear at home. This monitor allows the cardiologist to evaluate your pet’s heart rate and rhythm over a 24-48 hour period during normal activity.
This is used to better evaluate the frequency and severity of certain arrhythmias (abnormal rhythm) or to attempt to identify intermittent arrhythmias. It is also the best way to evaluate the response to anti-arrhythmic treatments.
Event Monitoring
Episodic collapsing or fainting spells can be caused by intermittent heart rhythm disturbances that may not be identified during the consultation.
An event monitor may be needed to attempt to evaluate the heart rhythm during the episode. Your pet wears this monitor at home and if you see an episode a button is pressed to mark this for later evaluation.
Once 2-3 events are marked this monitor is removed and the rhythm analyzed. This monitor can be worn for up to 2 weeks. Episodes must be frequent enough to warrant this test.
Thoracic Radiographs
Thoracic radiographs (chest x-rays) allow us to evaluate the size and shape of the heart and the lungs and their vessels. This is the best way to initially evaluate the cause of respiratory signs such as difficulty breathing and coughing. This is a necessary diagnostic test in those cases as both heart and primary lung diseases can cause respiratory signs.
If treatment for congestive heart failure is started this is the best way to determine whether congestive heart failure is controlled.
Interventional cardiology
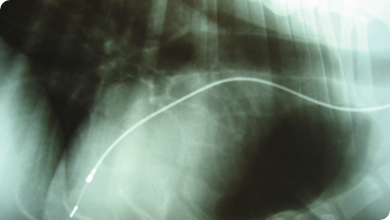
Pacemaker
In the case of arrhythmias in which the heart rate is too low, pacing of the heart with a pacemaker can be life-saving.
The battery is implanted under the neck muscles, and the lead is introduced in the heart via the neck vein (jugular vein).
Patent ductus arteriosus occlusion
Patent ductus arteriosus is a congenital heart disease in which a blood vessel allowing communication between the aorta and the pulmonary artery (the ductus arteriosus, present during the fetal life) failed to close at birth, leading to overflow of blood in the lungs and congestive heart failure early in the life of the patient
This vessel can be occluded via catheter-based technique, using an implant called ACDO. Once deployed, this device will close the ductus and allow a return to normal.
Balloon dilation of a stenotic pulmonic valve
The treatment of pulmonic stenosis, a congenital heart disease in which the pulmonic valve is malformed and unable to open correctly consists in introducing via the jugular vein a catheter with an inflatable balloon in the heart through the diseased valve and to inflate the balloon in order to “crack” open the valve.
If successful, this greatly improves the prognosis.
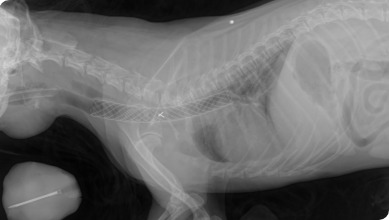
Tracheal stenting
In the case of severe tracheal collapse, with symptoms of respiratory difficulties and constant “honking”, tracheal stenting can greatly improve the situation.
This a non surgical technique, in which the stent is introduced via the larynx, using fluoroscopy to precisely position it
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is an advanced imaging technique where an ultrasound examination of the heart is performed. It allows imaging of the cardiac chambers, evaluate the function of the heart, heart valves and blood flow through the heart.
This is an essential exam to really assess the nature and severity of a heart disease.
This is a non-invasive diagnostic technique, which in general is very well tolerated. Most pets do not require any sedation but this will depend on their temperament. For most cases a small area is shaved on the chest behind each elbow to facilitate good imaging.

